This might sound cliche but mobile connectivity has indeed developed by leaps and bounds in the last five decades. In the 1980s, 1G delivered analog voice service. Then came the 2G in the early 1990s that introduced digital voice. 3G that came in the 2000s introduced mobile internet. 2010 onwards, 4G LTE (Long term evolution) found its applications in the era of mobile broadband.
5G is the next big thing in mobile networks that promises to take connectivity to the next technical advancement that includes a better use of spectrum,higher speeds, increased reliability and negligible latency.
The high data speeds and reliability will be a huge booster for businesses. Accessing cloud based services, augmented reality in online shopping experiences will now be a cakewalk for implementation.
The USP of 5G is that it is not limited to just mobile networks. 5G networks can be used by machines to communicate with other machines (IoT) and also by laptops and other handheld devices.The software infrastructure for 5G is fundamentally implemented in the cloud. Additionally, it will be completely open and software defined.
Software defined network(SDN) - What does that mean?
The main idea of a software defined network is to decouple, or physically separate the infrastructure of wireless networks from closed hardware network controller and shift it to an intelligent software running on the commodity hardware (your 5G enabled phone, laptop or any other device)
This decoupling enables the network control to become directly programmable. Also, the underlying infrastructure can be abstracted for applications and network services.
The SDN architecture is hailed for being
- Directly programmable
- Agile
- Centrally managed
- Configurable
- Vendor neutral with open standards
Unlike the seven layered OSI model, the SDN model has three layers.
The layers in SDN model are:
Application layer
Hosts the SDN applications and communicates with SDN enabled controllers via APIs.
Control layer
Controls and presents a logical map of the network for the applications running in the application layer
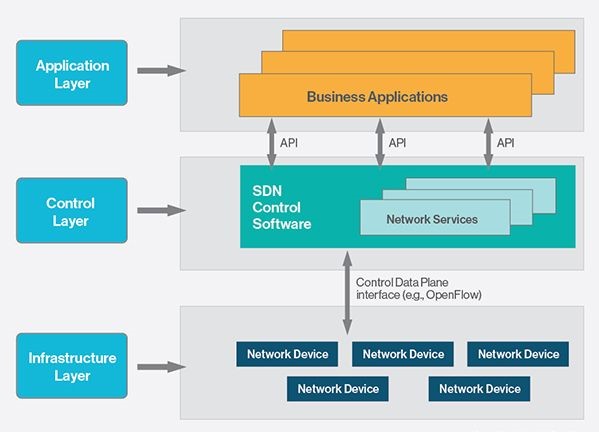
Infrastructure layer
Actual network hardware consisting of switches, routers and base stations
Network slicing
For SDN to truly act as a foundation for 5G, network providers should adopt what is known as network slicing. With network slicing, operators can create thousands of virtual, independent networks within the same physical network that connect from the device through to the application. Whether it’s connecting a handset to mobile broadband or a robot to an automation application, the network operator is able to guarantee service levels for the slice as if it were a distinct network.
With network slicing, each slice can have its own architecture, management, and security to support a specific use case. While functional components and resources may be shared across network slices, capabilities such as data speed, capacity, connectivity, quality, latency, reliability, and services can be customized in each slice to conform to a specific Service Level Agreement (SLA)
Network slicing is a purely software operation wherein several virtual networks can be created in a matter of minutes through automation. This is where software companies like Pace wisdom come into play, orchestrating, providing configuration and automation services.
Open source - a gateway for innovations
An open source software is the one whose design is in the public domain and wherein the community contributes to the development and maintenance of the program.
An open sourced technology is easily adopted by vendors and consumers alike, because of the magnitude of innovations and quicker resolution of issues. Hence, a combination of SDN and open source, in the form of 5G is sure to be well received and successfully implemented in the communication sector.
5G ushered transformations
As Ericsson predicts,5G has the potential to transform several industries in different ways, as listed below
- Connected cars that can exchange information and prevent collisions, all by themselves
- Faster deployment of emergency services to accident locations
- Autonomous production lines with fast response
- Increased use of IoT in factories, transforming them into smart factories
- Greater precision and realism in AR and VR devices
To sum it up
The world is moving at a pace where the existing network technologies like 3G and 4G are not sufficient to meet the demands. 5G is indeed the pathway for progress. This technology is very promising since the software infrastructure for 5G is open source and is software defined, guaranteeing oodles of innovation and swift advancements. The IoT sector will stand to benefit the most from this advancement which will eventually boost Smart city projects.



 Made with Superblog
Made with Superblog